Ancient Computer: The 2,000-Year-Old Device That Still Baffles
You've probably heard of ancient wonders like the pyramids and the Parthenon, but there's another marvel that's far more mysterious. Beneath the Mediterranean waves lay hidden a device so advanced, it shouldn't have existed in its time. The Antikythera Mechanism, with its complex system of bronze gears and astronomical calculations, challenges everything we thought we knew about ancient technology. Its discovery raises an intriguing question: what else were our ancestors capable of?
The Remarkable Discovery Off Antikythera
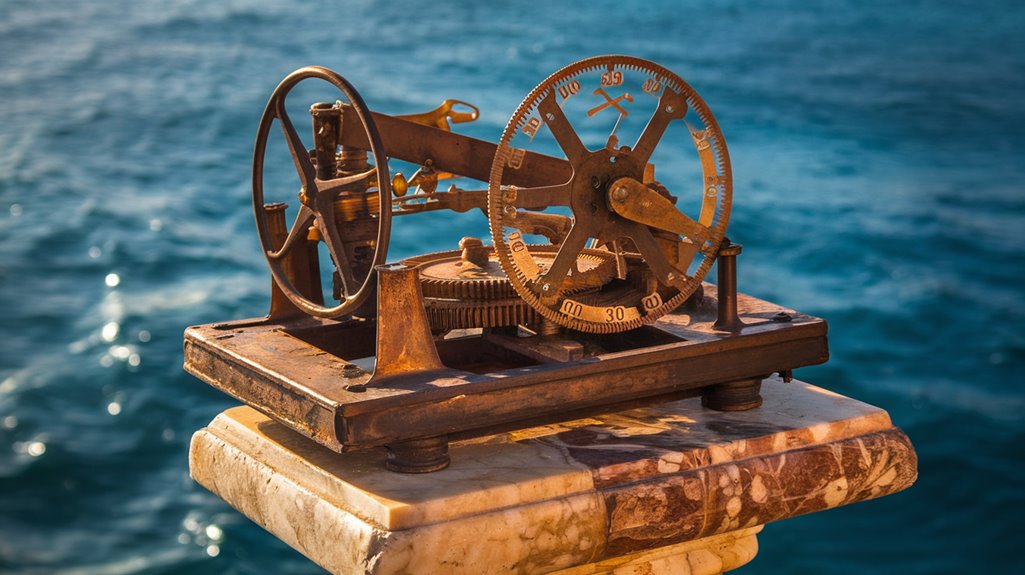

Just before Easter in 1900, Greek sponge divers made a discovery that would revolutionize our understanding of ancient technology.
During their diving discovery off the island of Antikythera, they found a shipwreck resting 45 meters below the surface, between Crete and mainland Greece. Recent expeditions have uncovered a second shipwreck approximately 800 feet south of the original site.
This underwater archaeology expedition initially yielded impressive bronze statues, marble sculptures, and various artifacts from around 70-60 BCE.
However, the most significant find wasn't recognized until May 17, 1902, when an archaeologist noticed something extraordinary – what appeared to be a rock had a gear wheel embedded within it.
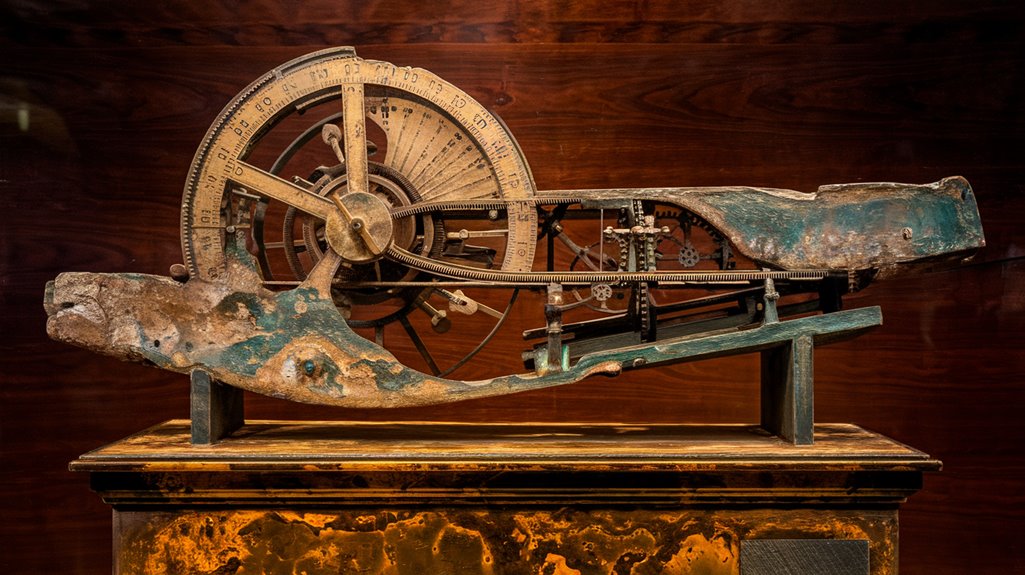
This corroded mechanism, found in three main parts with dozens of smaller fragments, would later prove to be one of the most mysterious and sophisticated devices ever discovered from the ancient world. The device was eventually identified as the world's first analog computer, capable of calculating complex astronomical positions.
Breaking Down the Ancient Marvel's Design
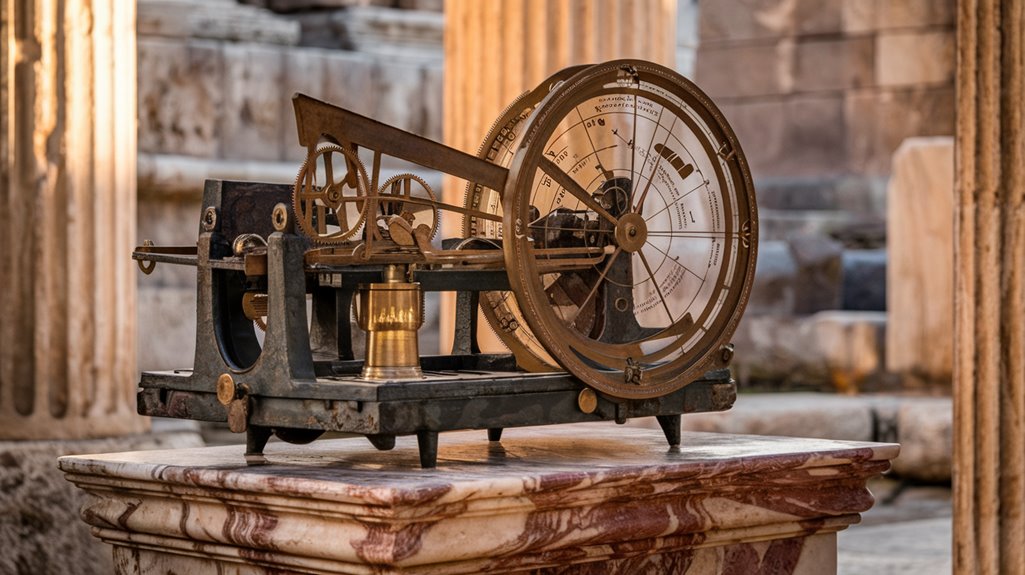
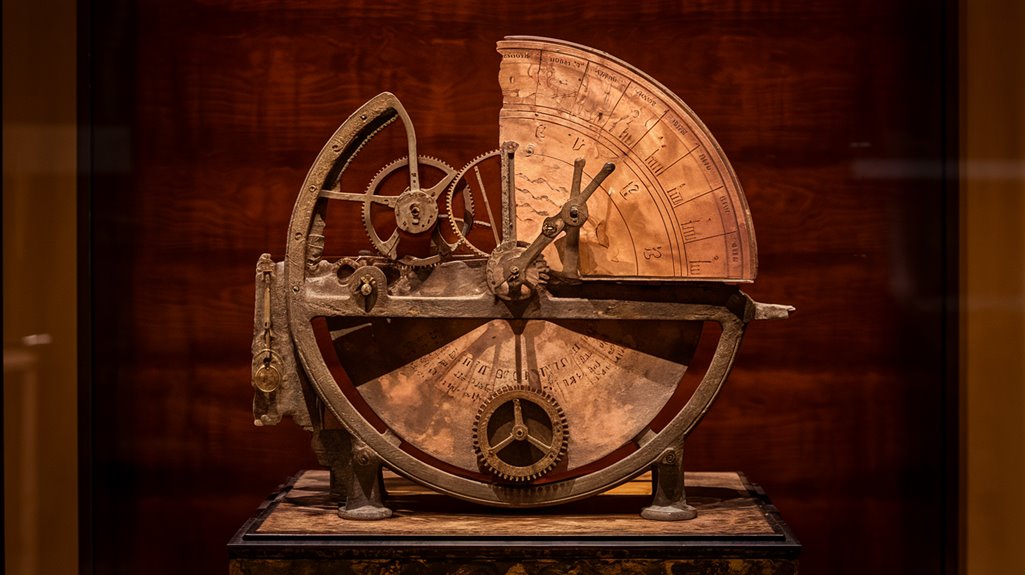
A mechanical marvel of the ancient world, the Antikythera mechanism's design reveals an extraordinary level of sophistication.
You'll find this shoebox-sized bronze device packed with an intricate system of about 30 gears, though some experts believe it may have contained up to 54 when complete.
The design intricacies extend beyond its gears. When you'd turn the hand-operated shaft, the astronomical mechanics would spring to life through a complex array of dials.
The front display featured the Sun and Moon's positions in the zodiac, while a half-silvered ball showed lunar phases.
The mechanism's epicyclic gearing mimicked celestial movements with remarkable precision, allowing you to predict astronomical events and eclipses decades into the future.
While initially thought to be a scientific tool, the device was actually designed as a luxury entertainment piece to impress wealthy guests with its astronomical predictions.
Through its calendar cycles and astronomical calculations, this ancient computer demonstrated technical capabilities that continue to amaze modern researchers. Discovered in 1901 off Antikythera, the device remained unnoticed for two years until an archaeologist identified its significance beneath the corrosion.
The Engineering That Defied Its Time
The engineering prowess behind the Antikythera mechanism stands unmatched for over a millennium after its creation.
You'll find mechanical precision in its 37 bronze gears, featuring teeth just a millimeter long, demonstrating a level of sophistication that wouldn't be seen again for 1,400 years.
What's truly remarkable is how this ancient computer performed complex celestial calculations. Greek divers discovered this shoebox-sized object while exploring a shipwreck in 1900.
Its largest gear, spanning 13 centimeters with 223 teeth, worked in harmony with dozens of smaller components to track the sun, moon, and planets. Recent research using statistical modeling techniques has revealed groundbreaking insights about its construction.
The device didn't just tell time – it predicted astronomical events and eclipses decades in advance.
Even more impressive, it tracked the four-year cycle of athletic games, similar to the Olympics, while displaying a detailed model of the Greek cosmos on its front plate.
Unlocking Secrets Through Modern Technology
Modern imaging technology has revolutionized our understanding of the Antikythera mechanism since its discovery in 1901. High-resolution scans have allowed researchers to examine 82 corroded fragments without causing damage, revealing intricate details about the device's lunar motion calculations and eclipse predictions.
Through interdisciplinary collaboration, teams of historians, astronomers, and engineers have pieced together this ancient puzzle. In 2021, experts at University College London created the first complete digital reconstruction of the mechanism's front panel, offering unprecedented insights into its original appearance and functionality. The reconstruction team successfully manufactured seven additional gears to complete their working model. The device was found to be capable of tracking five known planets, making it far more sophisticated than initially believed.
You'll find it fascinating that gravitational wave scientists have joined the investigation, adding fresh perspectives to our understanding of this remarkable device. Their work, combined with experimental archaeology and traditional tool recreations, continues to unveil the mysteries of ancient Greek technological capabilities.
Theories Behind Its Origins and Purpose
Building on recent technological insights, scholars have developed compelling theories about when and where this ancient marvel originated.
You'll find most experts dating its construction to the late second or early first century BC, with possible roots in Pergamon or Corinthian colonies. The device's sophisticated ancient astronomy features suggest inspiration from Archimedes' school of thought.
The complexity of its Hellenistic engineering, with over 30 intricate gears working in harmony, points to an even richer history of technological development. The wooden and bronze construction made it roughly the size of a shoebox. The discovery of this device in a Greek shipwreck revolutionized our understanding of ancient engineering capabilities.
You're looking at a device that wasn't just a one-off creation but likely the culmination of centuries of progress. Its primary purpose was remarkably ambitious: predicting astronomical events and tracking celestial movements decades in advance, while also monitoring athletic game cycles similar to the Olympics.










